The purpose of this report is to inform the public of the effects of consuming methamphetamines and what consequences this drug has on the brain and therefore mental health.
Mental health is an important part of today's society; it determines how a person reacts to social, emotional and psychological situations. Mental health helps us to decide how we react to various situations and how we determine stress, how someone relates to others and how everyday choices are made. It is very important to have good mental health as good mental health helps people to enjoy life and cope with everyday problems. Having poor mental health is dangerous and can have serious consequences on a person as it can complicate everyday activities and invites people to make irrational decisions.
This report will go over the effects methamphetamines have on mental health. Firstly by scanning through the background information about the production process. The report will go through the general chemical properties of methamphetamine. The report will then give an in depth explanation of how methamphetamine enters the bloodstream, the chemical reactions that happen during this process and then any interferences. Finally, an explanation of the brain's response to methamphetamine. This report will then discuss what effect methamphetamine have on mental health.
Mental health is an important part of today's society; it determines how a person reacts to social, emotional and psychological situations. Mental health helps us to decide how we react to various situations and how we determine stress, how someone relates to others and how everyday choices are made. It is very important to have good mental health as good mental health helps people to enjoy life and cope with everyday problems. Having poor mental health is dangerous and can have serious consequences on a person as it can complicate everyday activities and invites people to make irrational decisions.
This report will go over the effects methamphetamines have on mental health. Firstly by scanning through the background information about the production process. The report will go through the general chemical properties of methamphetamine. The report will then give an in depth explanation of how methamphetamine enters the bloodstream, the chemical reactions that happen during this process and then any interferences. Finally, an explanation of the brain's response to methamphetamine. This report will then discuss what effect methamphetamine have on mental health.
Background
IUPAC ID:N-methyl-1-phenylpropan-2-amine
Formula: C10H15N
Bioavailability: Oral: 70%, IV: 100%
Melting point: 170℃
Boiling point: 212℃ (414℉) at 760 mmHg
Metabolism:CYP2D6 and FMO3
Duration of action: 10-20 hours
Appearance: Clear chunky crystals
Solubility in water: base- insoluble, hydrochloride- soluble
Molecular mass:149.2337 g/mol
Methamphetamine is a synthetic chemical that is commonly manufactured in hidden illegal laboratories. It usually appears as clear white crystals or it can come in a white powder form.The raw materials that are used to make methamphetamine include Ephedrine or Pseudoephedrine, Red Phosphorus, Iodine, Lithium Acid, Anhydrous Ammonia, Caustic Soda and Hydrogen Chloride. A lot of these chemicals are highly dangerous and extremely toxic.
Methamphetamine is made when either ephedrine or pseudoephedrine is extracted from medication and then the chemical reaction is created by adding anhydrous ammonia and lithium acid or red phosphorus and iodine crystals with water. Both methods will create methamphetamine but at this stage, the chemical is too acidic to be used. The reaction between red phosphorus and iodine forms Hydriodic acid. After the Hydriodic acid is formed, the left over red phosphorus is filtered out of the chemicals then Caustic soda is added as a neutraliser for the methamphetamine. At this point, the chemical is at a liquid form so Hydrogen Chloride is added to turn it into crystal like substance. It is left to be dried out and then it is in its final form methamphetamine as shown in figure 1.
 |
| Figure 1: synthesis pathway for methamphetamine. Retrieved from: http://flipper.diff.org/app/items/info/6027 |
Methamphetamine can be smoked, snorted, injected, ingested orally or consumed using a patch and being absorbed through the skin (transdermally) . Regardless of the way the drug enters the body it is carried to the brain through the bloodstream. Orally administered drugs are absorbed through the stomach and the small intestine. The methamphetamine then passes through the liver and enters the bloodstream. This method of drug consumption is a lot slower than most ways. Injecting meth into the bloodstream is one of the fastest ways to cause a reaction as the drug is being injected directly into the bloodstream which is then taken directly to the brain. Transdermal consumption of illicit drugs isn't as common as injection or inhaling. Substances consumed this way are applied directly to the skin using a patch and absorbed into the bloodstream then to the brain. Methamphetamine that is inhaled as a gas penetrate the lining of the esophagus and lungs quickly being absorbed into the bloodstream. Methamphetamine being smoked does not get absorbed as quickly as gases. The smoke particles attach to the lungs and are then absorbed.
The distribution of methamphetamine happens via the circulatory system, once methamphetamine has entered the bloodstream the heart pumps the blood throughout the body carrying the substance with it. Before the substance can enter the central nervous system, it passes the blood brain barrier. Which is a system of tightly woven capillaries that are designed to prevent poisons and dangerous substances from entering the brain. Methamphetamine is specifically designed to pass through the barrier.
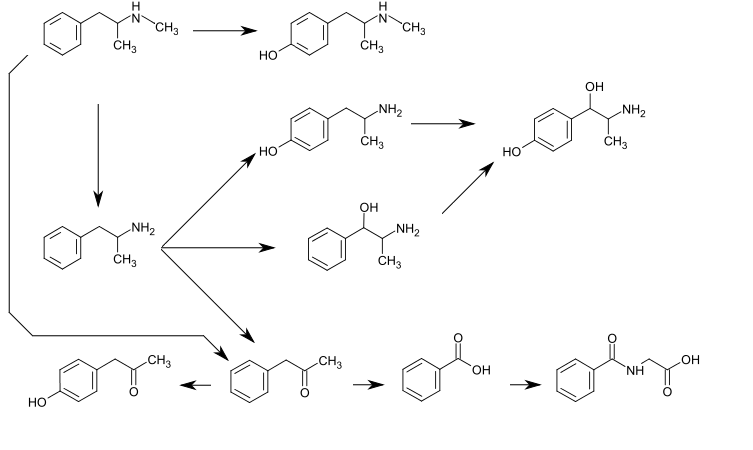 |
| Figure 2: Metabolic pathway of Methamphetamine in humans. Retrieved from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Methamphetamine#Synthesis |
Methamphetamine can be extremely damaging to many organs due to long term use of the substance. Methamphetamine can cause a lot of irreversible harm like increased heart rate and blood pressure, it can cause damaged blood vessels in the brain which can cause strokes and an irregular heartbeat. Using the substance for a long period of time can cause permanent serious injuries to your liver, kidneys and lungs.
In an ordinary nervous system, electrical signals are received and sent through neurons. The signal at the end of the neuron triggers the release of neurotransmitters into the gap of one neuron and the beginning of the next neuron. This gap is called the synapse. Neurotransmitters are released into the synapse and then bonded to the receptors located on the postsynaptic neuron. The binding of the neurotransmitter to the receptor triggers a response in the neuron. The neurotransmitters left in the synapse are reabsorbed by the presynaptic neuron which stops the postsynaptic neuron from being further triggered.
When methamphetamine enters the brain's neurons, the neurons release extra amounts of dopamine into the synapse too much dopamine causes an individual to experience uncontrollable movement and twitching but at the same time they experience great amounts of pleasure. Increased dopamine levels can also create hallucinations and delusion which makes the person affected display similar characteristics to individuals with schizophrenia. The first time methamphetamine is used the person will experience an ultimate high but the next time it is consumed there isn't as much dopamine left so the user keeps taking more and more of the drug to achieve the same effects as the first high but this cannot be achieved as methamphetamine destroys the transporters and causes the receptors to withdraw, lowering their dopamine levels.
With methamphetamine being introduced to the nervous system, neurotransmitters are incapable of being reabsorbed into the presynaptic neuron. This happens because the methamphetamine blocks the passage which the chemicals are taken through, causing neurotransmitters to flood the synapse and trigger responses in the postsynaptic neuron. Methamphetamine effects four neurotransmitters, dopamine, serotonin, epinephrine and norepinephrine.
Discussion
Methamphetamine has a severe impact on the user's mental health as the drug interferes with the users dopamine levels and damages the receptors and transmitters. This causes them to fail at producing the correct amount of dopamine and can develop complications when the brain tries to use what dopamine it has due to methamphetamine blocking the neurons.
One of the most common mental illness with relation to methamphetamine usage is the ‘meth induced psychosis’. Psychosis happens when someone experiences both hallucinations and delusions, it is called a meth induced psychosis because the person is experiencing these symptoms due to the use of methamphetamine. Up to 46 percent of users have reported a meth induced psychosis. Methamphetamine users who suffer this illness find themselves out of touch with reality which causes aggressive behaviour, delusions, paranoia and other obsessive behaviours which is the result of long term methamphetamine use. These behaviours start to wear off for some users as they start to come down from the drug but there are many people who experience these psychotic symptoms when they’re not under the influence of methamphetamine, some users can be left in a permanent state of psychosis.
During the withdrawal stage of methamphetamine use, users will experience paranoia, anxiety, depression and panic attacks which can last up to weeks. This often results in the user relapsing and continuing their use of methamphetamine.
People who have a history of mental illnesses report having more severe symptoms once they began using methamphetamine. Users who have pre-existing depression find themselves more vulnerable to self harming and suicidal thoughts. Studies have shown that the antidepressant bupropion can reduce cravings for methamphetamine and is also effective in managing the depressive effects.
Over 75 percent of users have reported major symptoms of anxiety disorder. Anxiety disorders can be permanent even if the user is no longer using methamphetamine. Treating anxiety disorders amongst methamphetamine users can be quite difficult as a lot of effective prescription medications, such as benzodiazepines, to treat the anxiety disorder can be addictive and users can become secondarily addicted.
Conclusion
In this report the effects of methamphetamine on mental health was discussed in great detail. It talked about the materials that are used in the production of methamphetamine as well as information explaining how methamphetamine enters the bloodstream, then the brain and the reactions that are caused. There is also an in depth explanation of how methamphetamine affects your brain's neurotransmitters and finally it talks about what effects methamphetamine has on a user's mental health.
The usage of methamphetamine blocks off the dopamine neurons causing dopamine to uncontrollably leak out into the synapse and not return to the neurons causing a great deal of pleasure which lasts up to around 10-20 hours. When the brain starts to come down the user experiences major withdrawal symptoms which causes them to experience psychosis, depression, anxiety, paranoia and many other aggressive behaviours which can last from days, weeks or these symptoms can be permanent. These are all the effects methamphetamine has on a user's mental health.
Public Education Piece
My Public education piece is a slide show to inform the general public about the effects methamphetamine has on mental health.
References
Wikimedia commons (3 Jun. 2010.). File:Methamphetamine from ephedrine with HI en.png - Wikimedia Commons. Commons.wikimedia.org. Retrieved from https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Methamphetamine_from_ephedrine_with_HI_en.png
National Institute On Drug Abuse (last update, september 2013.). What are the long-term effects of methamphetamine abuse?. Drugabuse.gov. Retrieved from https://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/research-reports/methamphetamine/what-are-long-term-effects-methamphetamine-abuse
Eric Patterson (17 Jul. 2012.). The Effects of Crystal Meth Use. DrugAbuse.com. Retrieved from https://drugabuse.com/library/the-effects-of-crystal-meth-use/
American Addiction Centers (n.d.). Effects of Crystal Meth on the Brain and Central Nervous System. American Addiction Centers. Retrieved from https://americanaddictioncenters.org/meth-treatment/effects-on-the-brain-and-cns/
Formulation (27 Apr. 2016.). MANUFACTURING AND MATERIALS TO MAKE SHABU (METHAMPHETAMINE). Formulation.vinensia.com. Retrieved from http://formulation.vinensia.com/2011/04/manufacturing-and-materials-to-make.html
The Recovery Village (n.d.). The Dangers of Methamphetamine: Ingredients and How It's Made. The Recovery Village. Retrieved from https://www.therecoveryvillage.com/meth-addiction/dangers-methamphetamine-ingredients-made/
James Bullen (20 Feb. 2017.). What happens to your body when you use ice?. ABC News. Retrieved from http://www.abc.net.au/news/health/2017-02-20/ice-what-happens-to-your-body-when-you-use-the-drug/8275654
National Institute On Drug Abuse (n.d.). What are the long-term effects of methamphetamine abuse?. Drugabuse.gov. Retrieved from https://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/research-reports/methamphetamine/what-are-long-term-effects-methamphetamine-abuse
N.a (n.d.). methamphetamines reaction pathway - Google Search. Google.com.au. Retrieved from https://www.google.com.au/search?safe=strict&biw=1366&bih=662&tbm=isch&sa=1&q=methamphetamines+reaction+pathway&oq=methamphetamines+reaction+pathway&gs_l=psy-ab.3...6795.10052.0.10311.12.11.0.0.0.0.437.1713.2-1j3j1.5.0....0...1.1.64.psy-ab..9.0.0....0.8eiIbBdBM_o#imgrc=UDPQp5CHHAkNGM:
Flipper (n.d.). Methamphetamine Synthesis and Effects. Flipper.diff.org. Retrieved from http://flipper.diff.org/app/items/info/6027
Wikipedia Contributors (4 Nov. 2017.). Methamphetamine. Wikipedia, the Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Methamphetamine#Synthesis
Sunrise House (n.d.). The Path Drugs Take Through the Body | Sunrise House. Sunrise House. Retrieved from https://sunrisehouse.com/cause-effect/path-drugs-take-body/
Contributors (n.d.). Meth Addiction and Mental Illness. Mentalhelp.net. Retrieved from https://www.mentalhelp.net/articles/meth-addiction-and-mental-health-problems/
N.a (n.d.). How does methamphetamine (meth) damage neurons?. Biology.stackexchange.com. Retrieved from https://biology.stackexchange.com/questions/58050/how-does-methamphetamine-meth-damage-neurons
Methamphetamine (27 Apr. 2012.). The Nervous System. Methamphetamine. Retrieved from https://methiscool.wordpress.com/nervous-system/
Kaw (19 Jul. 2016.). What is Meth Psychosis?. The Cabin Chiang Mai. Retrieved from https://www.thecabinchiangmai.com/what-is-meth-psychosis/
Brain and behaviour (7/11/2011). Brain and Behavior - YouTube. Youtube.com. Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T-duk-PiIXo

Post a Comment
Thanks for your contribution. Our students appreciate your comment.